CML2 自定义节点
一、Custom VM Images Overview
《Cisco Modeling Labs 2 安装&使用》一文中提到CML2还支持其他的第三方镜像,并且演示了如何新建自定义镜像。在CML2中自定义镜像需要用到两个组件,分别是Node Definitions和Image Definitions。本文将继续介绍如何创建Image Definitions以及Node Definitions,图1-1展示了这两个组件所在的位置。
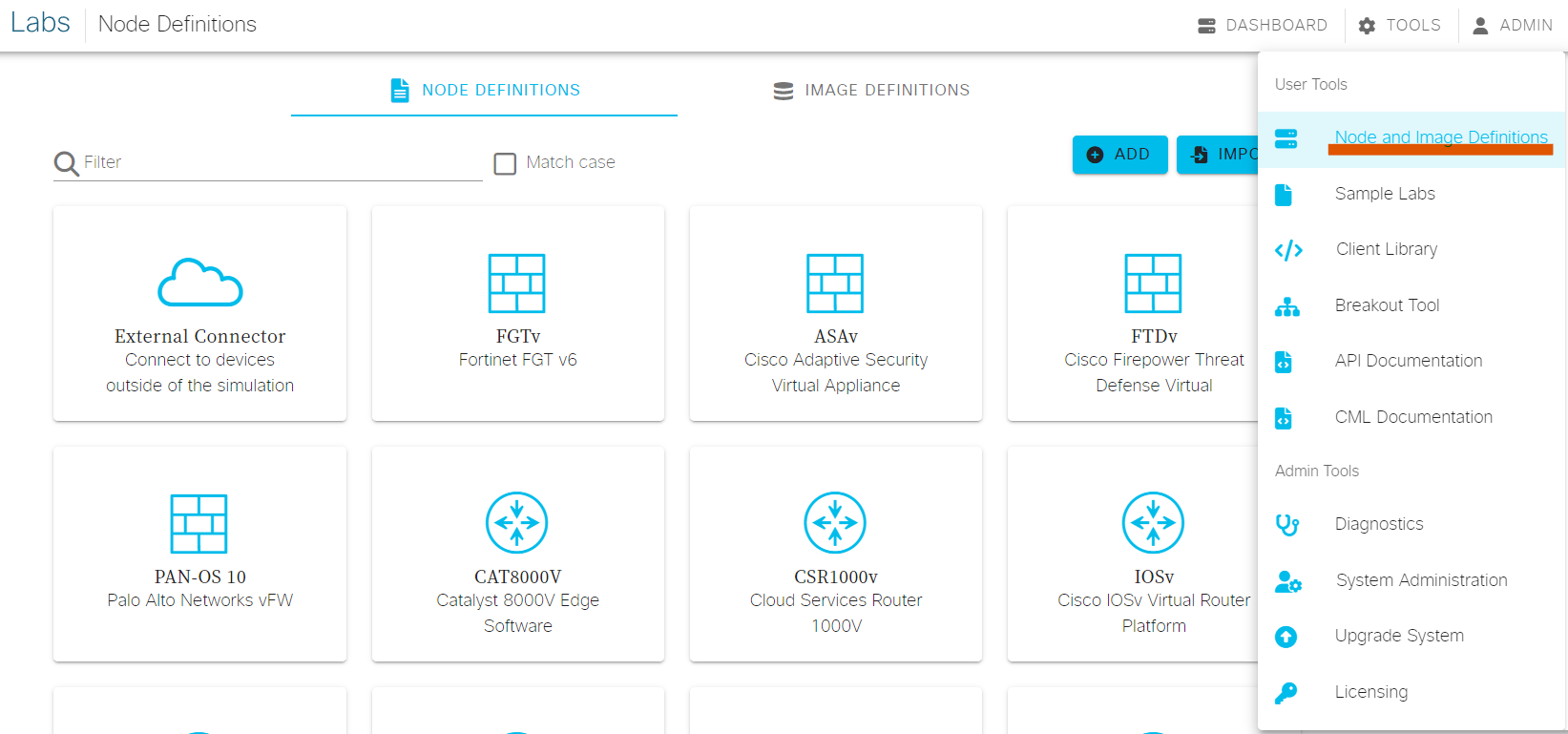 图1-1
图1-1
CML2中的Image Definitions代表了一种版本的镜像。镜像定义包括id、Label、Description、Disk Image、Node Definition,其中Disk Image所选择的镜像版本是通过MANAGE上传的,Node Definition则是用于将该Image Definition关联到某一个虚拟设备系列。
CML2中的Node Definitions代表了一种虚拟设备系列,虚拟设备系列可以存在多个版本镜像(即需要提前创建多个Image Definitions)。例如创建了一个叫ASAv的Node Definition,其关联了两个Image Definitions,分别是ASAv915、ASAv916。
二、Image Definitions
进入Node and Image Definitions后,选择IMAGE DEFINITIONS。可以在图2-1中看到8个已经定义好的Image Definitions(先不管),其中MANAGE用于管理上传的qcow2镜像,ADD用于定义新的Image Definitions。
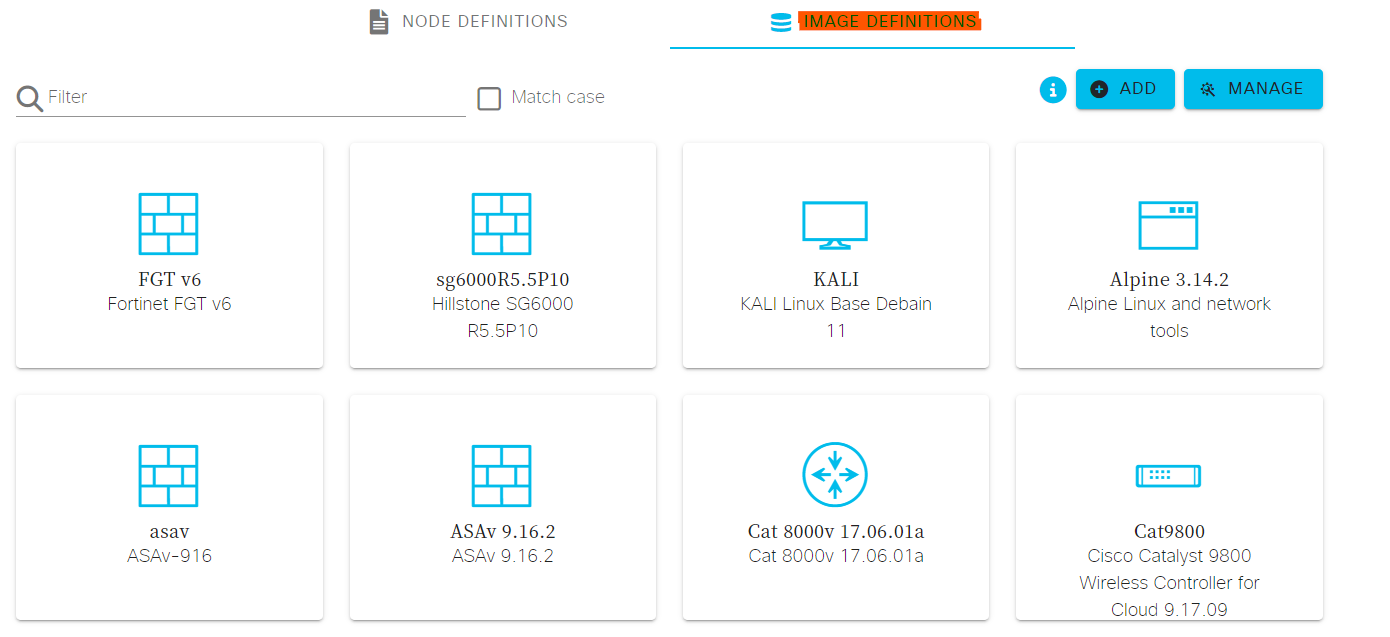 图2-1
图2-1
1、Upload Image
通过点击UPLOAD IMAGE选择需要上传的镜像。上传完成的镜像会在Uploaded Images中展示,如图2-2。
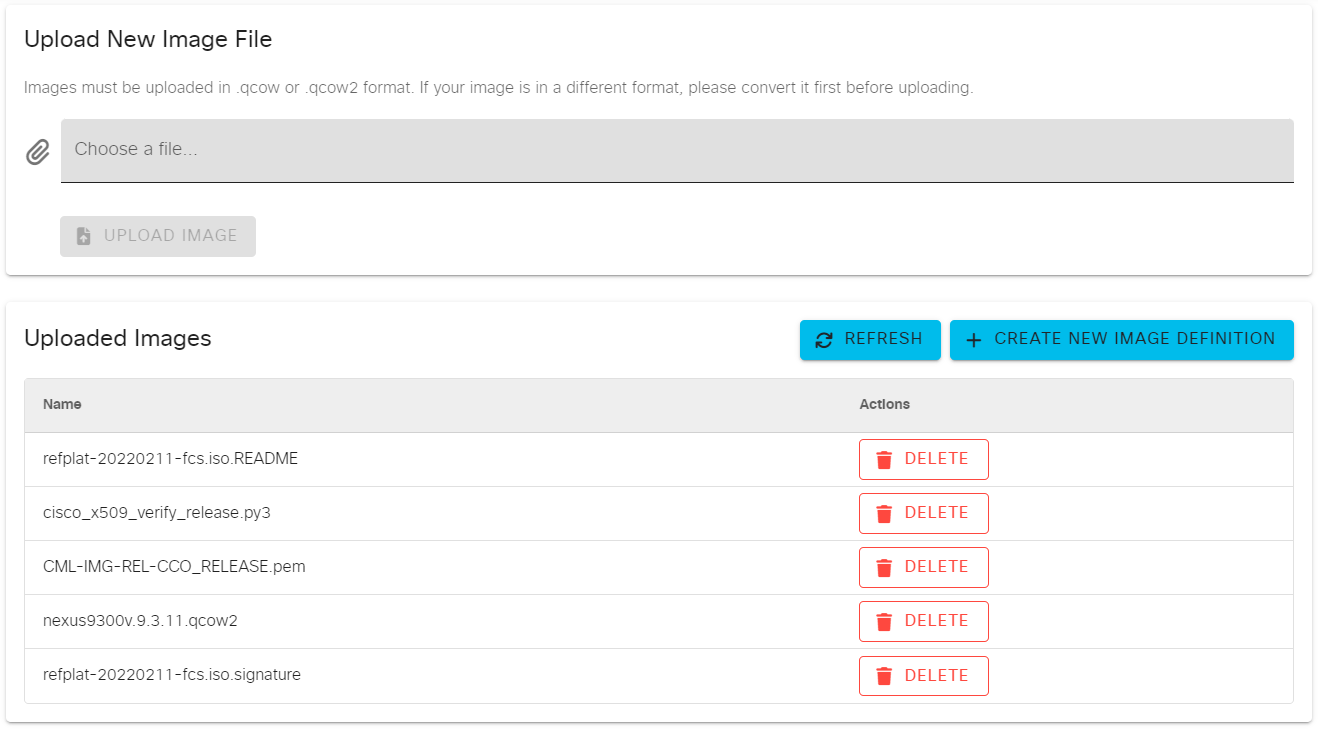 图2-2
图2-2
2、About Image Definition Parameters
开始创建Image Definition之前,需要先来了解下创建它的相关参数含义。
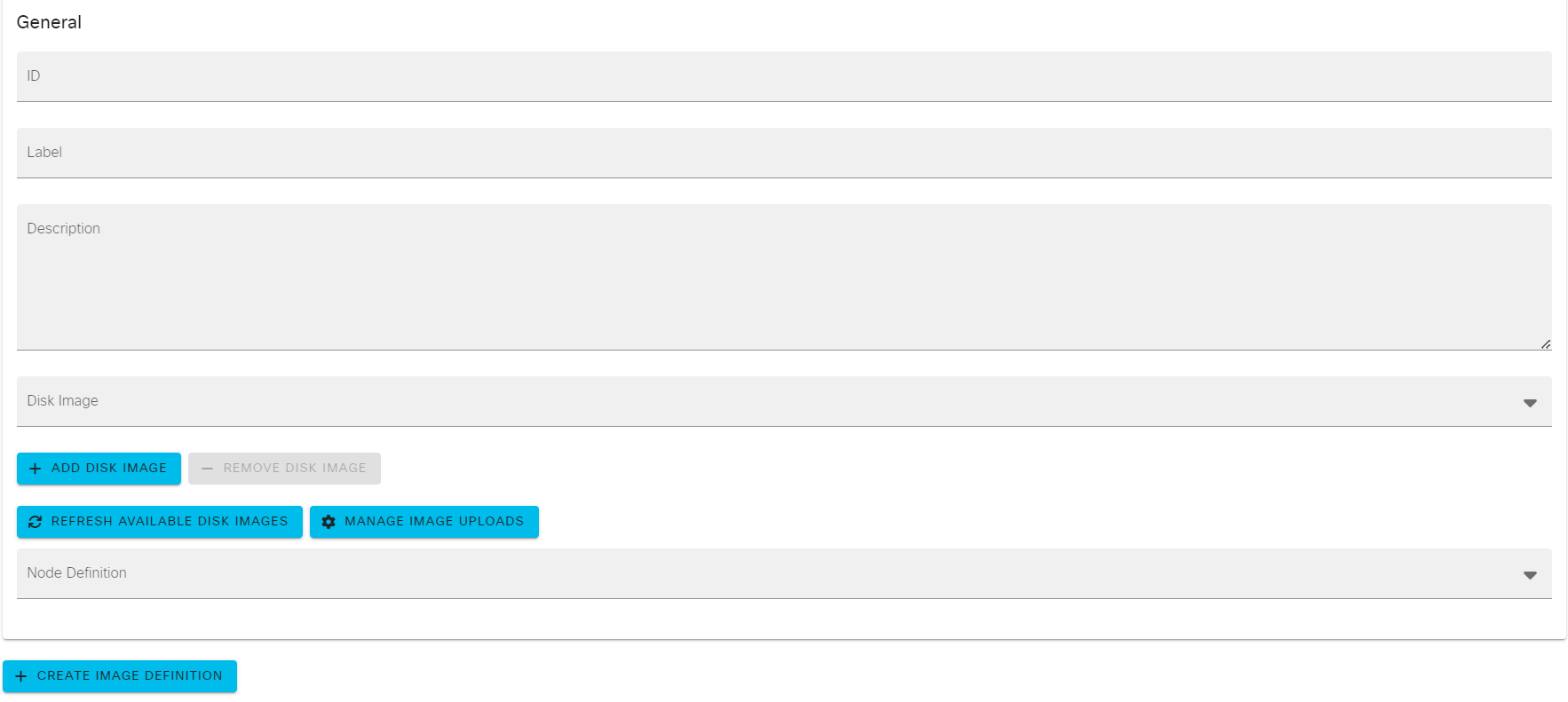 图2-3
图2-3
创建Image Definition时有如下参数:
ID:CML2中的每一个镜像都具备的唯一识别码,创建ID时不可以包含空格键。
Label:标签会在CML2图形化界面中展示(在进行镜像选择时会展示),建议使用镜像系统名和版本,例如IOSv 15.6(3)。
Description:对镜像的更加详细的说明(例如镜像中的常见操作、镜像使用的硬件资源、镜像的用户名密码),该参数是可选的。
Disk Image:用于选择在Upload Image阶段上传的某一种版本的镜像。
Node Definition:选择该镜像用于关联到某一种虚拟设备系列,例如ASAv915、ASAv916被关联到ASAv虚拟设备系列。
以上参数中除Description参数外,均需要设置的。以下参数通常在Node Definition中被定义,除非多个不同版本的Image Definitions之间所需要的硬件资源不同时,才会定义这些参数,以区别对待:
Memory:此镜像所需要的内存量,通常参考镜像安装时所需的内存量。
CPUs:此镜像所需要的虚拟CPU数量,通常参考镜像安装时所需的虚拟CPU数量。
CPU Limit:从该镜像创建的虚拟机被允许使用已分配CPU的百分比,通常设置100%。CPU Limit通常用于大型拓扑中各虚拟机的启动,因为大型拓扑中通常有很多使用大量CPU的虚拟机(例如IOSv和IOSvL2),所以CPU Limit是为了防止其他镜像因为CPU资源被占用而无法开机的情况的一个保底方案。如果Boot Timeout设置120s超时,CPU Limit设置25%,那么CML会把超时值自动调整为480ms。
CML2中消耗CPU较多的镜像有两种类型:持续轮询类型以及资源密集类型。持续轮询类型的镜像主要是IOSv、IOSvL2,资源密集类型的镜像主要是IOS XRv 9000。
通过案例说明使用CPU Limit功能与否对于资源消耗的不同:通过将CPU Points作为对CPU容量的抽象表示,为每个CPU内核分配100 CPU Points。换句话说如果为CML2服务器分配了8 * vCPU,那么CML2的CPU容量则为800 CPU Points。案例展示:一个节点拥有一个CPU且没有设置CPU Limit,那么它需要100 CPU Points才能启动;一个节点拥有一个CPU且设置CPU Limit=25%,那么它需要25 CPU Points就能启动;一个节点拥有两个CPU且设置CPU Limit=25%,那么它需要50 CPU Points就能启动。
Data Disk Size:此镜像所需要的数据磁盘容量,单位为GiB,通常参考镜像安装时所需的磁盘容量。数据磁盘会被添加到虚拟机所需要的系统磁盘之外,例如SD-WAN控制器则需要将其数据库存储在第二个磁盘上。
Boot Disk Size:此镜像所需要的系统磁盘容量,单位为GiB,通常参考镜像安装时所需的磁盘容量。系统磁盘通常存放操作系统并被标记为可启动的磁盘。值得注意的是用于启动虚拟机的系统磁盘容量必须≥ qcow2 文件自身的大小,换句话说系统磁盘大小至少应该和qemu-img info报告的虚拟大小一样大。
具备以上参数后便可以成功创建一个镜像了。
三、Node Definitions
创建完Image Definitions之后,接下来开始创建Node Definition之前,需要先来了解下创建它的相关参数含义。
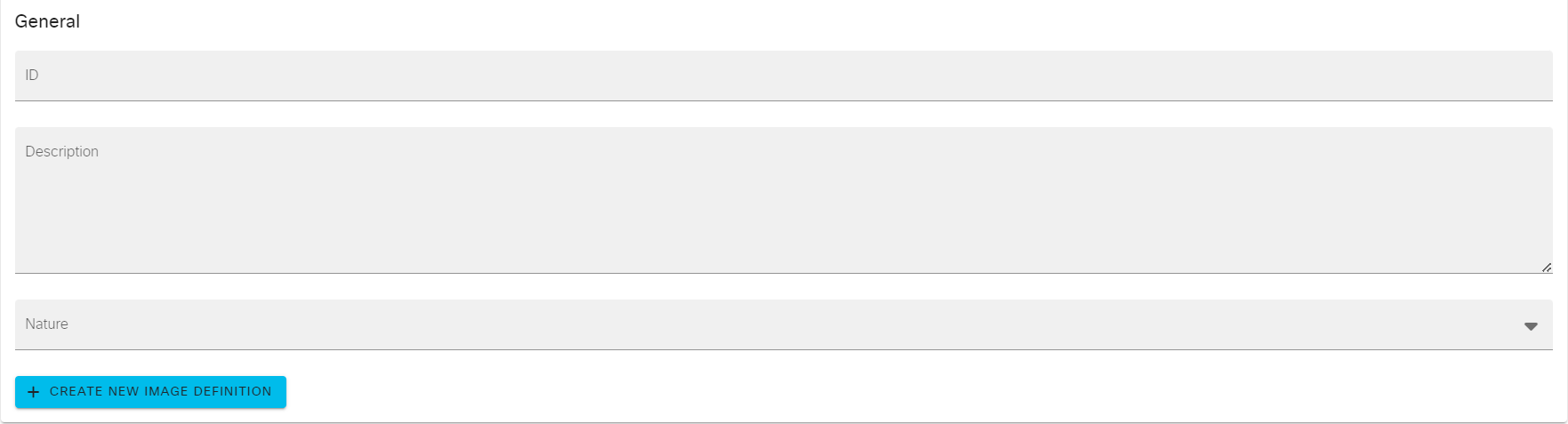 图3-1
图3-1
General参数:
ID:CML2中的每一个虚拟设备系列都具备的唯一识别码,创建ID时不可以包含空格键。
Description:对虚拟设备系列的更加详细的说明,该参数是可选的。
Nature:指虚拟设备系列在网络中所扮演的角色,通常的角色有Server、Firewall、Switch、Router等。
 图3-2
图3-2
User Interface参数:
Visible:启用后Workbench->Add Nodes会显示该虚拟设备系列,通常启用。
Description:对节点定义的描述,支持Markdown格式,可选参数。
Prefix:使用该节点创建的虚拟机会带一个默认的命名前缀,该参数就是用于创建默认命名前缀的。通常的格式为虚拟设备系列加上一个"-",例如某节点前缀为asav-,则创建三台asav虚拟机的命名分别是asav-1、asav-2、asav-3。
Icon:用于指定该节点的图标,通常和Nature参数相对应。
Label:用于在Workbench->Add Nodes中显示标签名。
 图3-3
图3-3
Linux Native Simulation参数:该部分的参数用于描述所有虚拟化属性。
Domain Driver:此节点的虚拟化驱动,始终选择KVM。
Simulation Driver:CML仿真驱动配置文件;该参数通常选择Server,Nexus 9000v的自定义节点驱动配置文件请选择nxosv9000。
Disk Driver:此节点的磁盘驱动,通常参考镜像安装时所需的磁盘驱动。
Memory:参考Image Definition中的Memory参数释义。
CPUs:参考Image Definition中的CPUs参数释义。
CPU Limit:参考Image Definition中的CPU Limit参数释义。
Network Driver:此节点的网卡驱动,通常参考镜像安装时所需的网卡驱动。
Data Disk Size:参考Image Definition中的Data Disk Size参数释义,该参数可选。
Boot Disk Size:参考Image Definition中的Boot Disk Size参数释义,该参数可选。
Video Model(可选):此节点的显卡,通常选择默认值,某些节点可能需要设置特定型号(可供选择的显卡类型std、cirrus、vmware、qxl、xenfb、tcx、cg3、virtio、none)。
对于有图形化需求的节点,可以设置Standard VGA 或 Cirrus VGA(设置完成后,CML2会提供VNC选项);
对于仅依赖串口控制台需求的节点,直接选择none。
Video Memory(可选):设置了Video Model后,需要设置显存,单位为MiB。显存值必须设置为非零值,通常设置为16/32MiB够用即可。
 图3-4
图3-4
Interfaces参数:该参数需要参考镜像安装时的默认接口数、最大接口数、接口命名规则。
Has a Loopback Interface:此节点如果应该需要Loopback接口则启用它,反之禁用。
Loopback Name:Loopback接口名;例如Linux下的Loopback名为lo,该参数可选。
Number of serial ports:虚拟机串行接口总数;即使没有串行接口,该值也不应该为0,该值范围1-8。一般情况下思科设备具备2个串行接口,分别是Console和AUX,Linux可以使用串行接口做文本控制台,如果镜像安装时特别注明多个串行接口时需要按照说明填入数值。
Default number of physical interfaces:默认物理接口数,该值参阅对应的镜像安装需求。
最后设置该节点在CML2图形化界面中的接口,接口数量和命名规则按照实际Image中规定的来:
接口数量:如果接口数量镜像中定义了4个,但是你在此处只命名了3个,那么CML2图形化界面中就只显示3个接口。
接口命名规则:不同的设备或相同设备不同速率的接口命名规则不同。例如思科万兆光口TenGigE0/0、数据中心交换机Ethernet0/0,Linux接口eth0等。注意此字段填充的字符长度有要求。
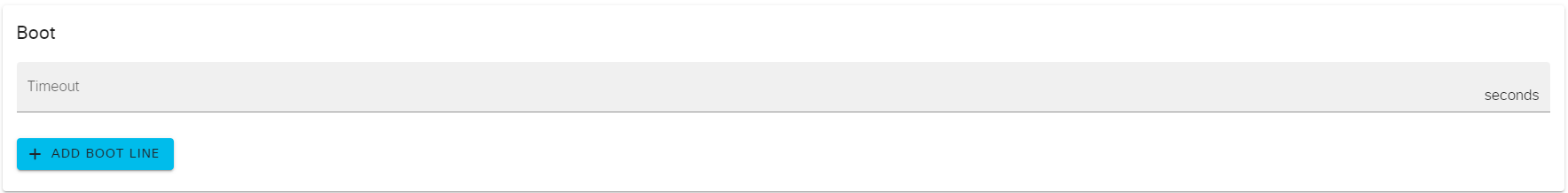 图3-5
图3-5
Boot参数:节点在启动时的一些设置,通过设置Timeout和ADD BOOT LINE参数可以使得节点启动完成后状态显示☑️。
Timeout:节点从启动中(节点状态显示🔄)到启动完成前(节点状态显示☑️)所需等待的最长时间,单位为秒。
ADD BOOT LINE:CML2会检查节点的Console控制台,如果出现引导行字符串就会认为节点已经启动完成,那么这个引导行字符串就是在该参数中定义。以下为案例:
例1:IOSv启动过程中,如果检查到Console控制台字符串为 %PLATFORM-5-SIGNATURE_VERIFIED: 和 Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog? 时就会被判断为节点启动完成。
例2:USG启动过程中,如果检查到Console控制台字符串为 Loading /boot/busybox-initrd-static...ok 时就会被判断为节点启动完成。
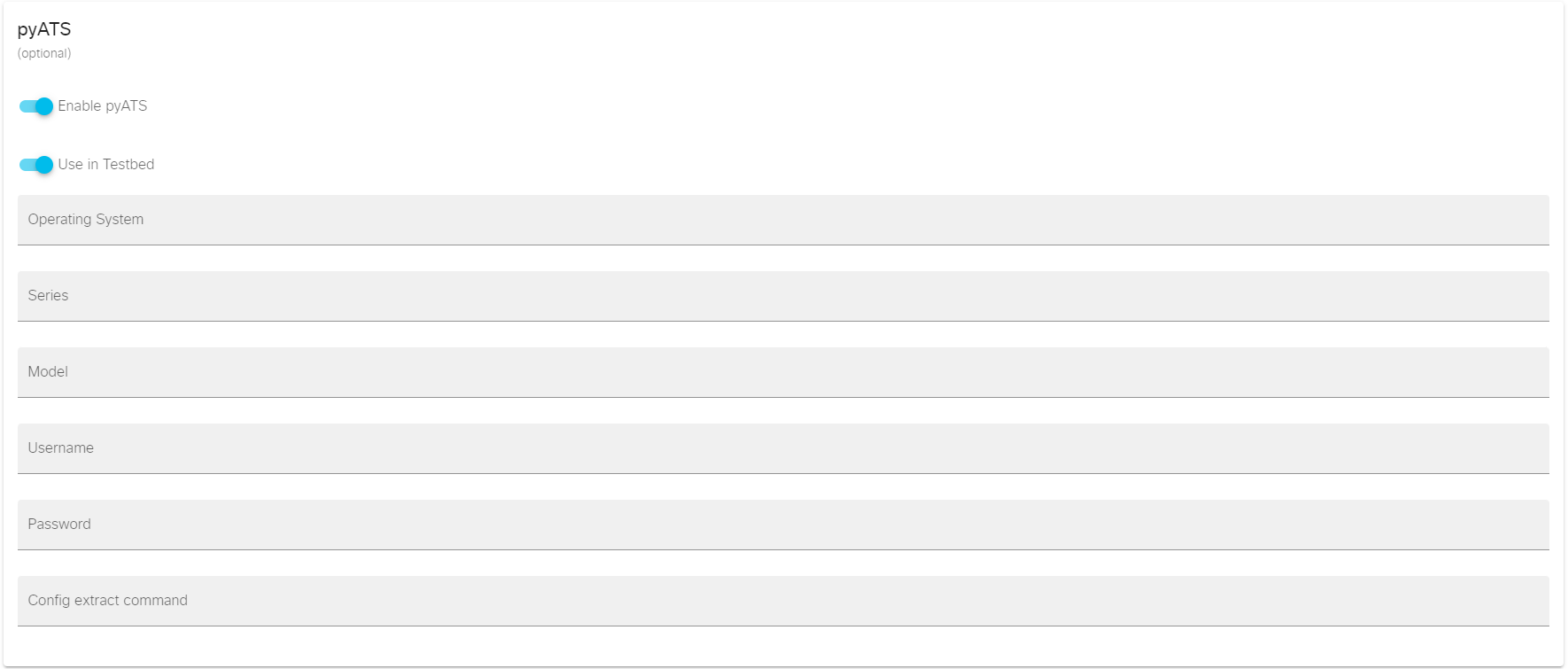 图3-6
图3-6
pyATS参数:pyATS 是思科公司推出的开源 Python 框架,用于创建和运行自动化网络测试。CML2提供了pyats_testbed API,可以为Lab生成测试平台定义,以便与pyATS测试一同使用。为节点定义启用pyATS支持和在测试平台中使用,CML2就会在Lab的pyATS测试平台中包含与该节点定义相关的节点,并填写所有正确的设备特定参数。
注意如果要在此节点定义相关的节点上使用配置提取,则必须启用pyATS。如果不打算使用pyATS进行配置提取以外的其他操作,可以启用"Enable pyATS",并禁用"Use in Testbed"。
Enable pyATS:如果 pyATS 支持这种类型的设备,请启用pyATS功能,否则禁用。
Use in Testbed:如果启用,则此节点定义相关的节点将显示在导出的测试平台定义中;如果禁用,该设备将从pyATS测试平台中省略。
Operating System:根据pyATS定义的操作系统名称。例如IOSv操作系统类型就是"ios"。
Series:设备系列,该参数可选且通常不需要设置。
Model:设备型号,该参数可选且通常不需要设置。
Username:pyATS登录设备时的登录名。
Password:pyATS登录设备时的密码。
Config extract command:从Lab中使用Extract Configuration功能提取节点当前配置时,CML将在与此节点相关联的节点上使用此配置提取命令。需要先Enable pyATS。如果有命令可以获取节点的当前配置,请在此处输入该命令。
有关pyATS支持的设备、操作系统、系列、型号参考official pyATS/Unicon documentation.
 图3-7
图3-7
Property Inheritance参数:默认情况下Lab中新建的节点会采用Node Definition中定义的值,而属性继承参数可以使得节点定义继承Image Definition或者通过节点定义的单个节点属性值。对于继承的属性,CML2首先检查该属性是否在节点上设置,是的话直接使用该值,否则检查Image Definition中定义的值,如果Image Definition中没有该值的定义则会使用Node Definition中定义的该值。
举个粒子:假设IOSv's Node Definition指定RMA为512 MiB,如果Image Definition中定义的是需要768 MiB RMA的IOSv版本的镜像,最后创建的节点将以Image Definition中定义的768 MiB为RAM设置。如果在Lab中通过单个节点的属性修改为1024 MiB,那么该节点将以1024 MiB的RAM来运行,当然此方式只适用于该节点,不适用于采用节点定义的其他节点的值或者Image Definition中定义的值。
可以继承的属性有:RAM、CPUs、CPU Limit、Boot Disk Size、Data Disk Size。
CML2为节点提供基本的存根配置(stub configurations),根据节点类型可以生成配置(主机名、激活接口、用户配置、登录配置,不支持生成IP和任何路由协议及高级配置)。Configuration Generator主要负责存根配置,Configuration Generator仅为clean Nodes和wiped但是尚未启动的节点生成配置。
Ubuntu和Core OS的存根配置可以直接利用cloud-init配置,参阅 cloud-init configuration examples。
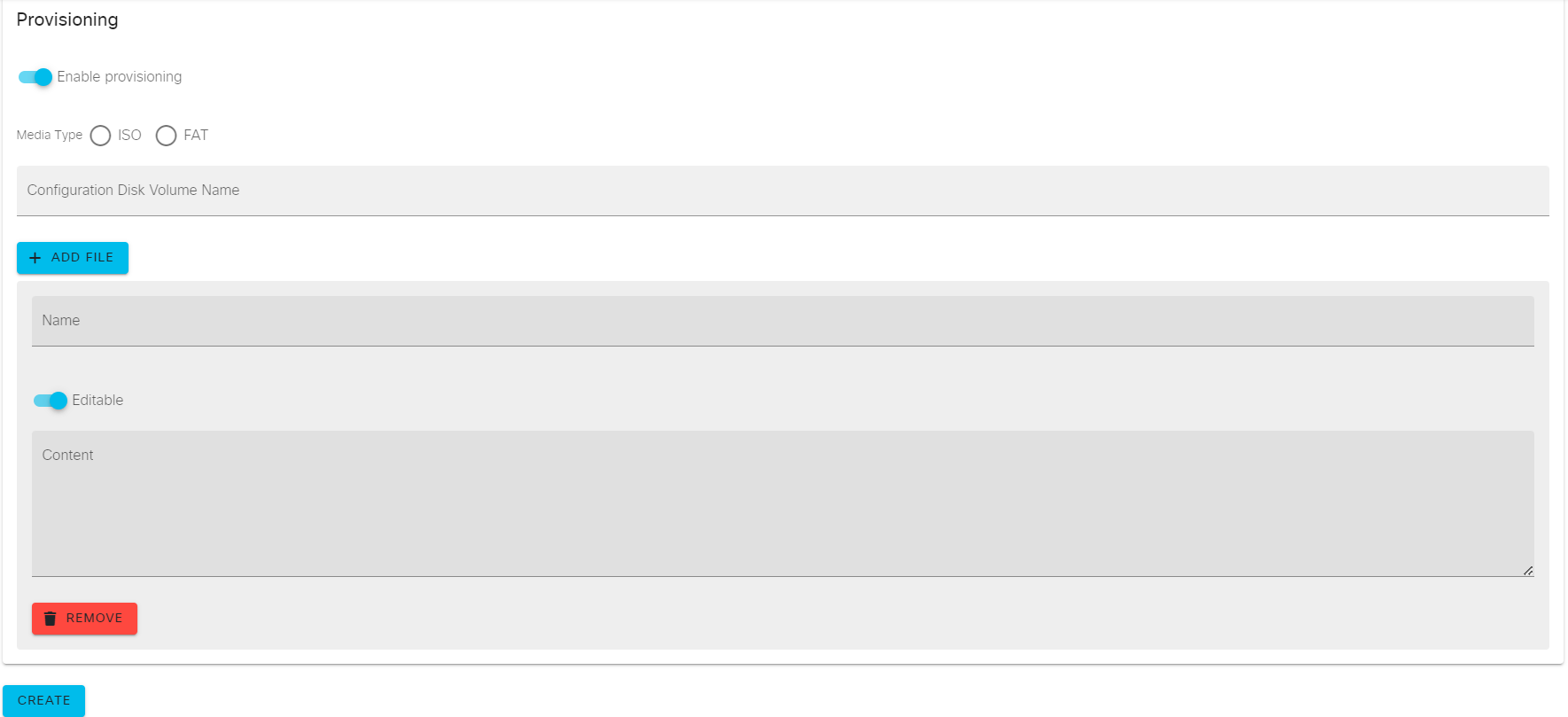 图3-8
图3-8
Provisioning参数:如果设备配置了Bootstrap Configuration,需要在此处指定配置的详细信息(建议查阅相关镜像安装和配置文档,了解引导配置如何工作)。
Enable provisioning:启用Provisioning,CML2将采用此处或Workbench ->Node's Config选项卡指定的引导配置,将其转换成节点虚拟机内的ISO9660(CD-ROM)或FAT卷。节点虚拟机启动后,会从该卷中读取数据并执行所有初始化配置。
Media Type:用于存储初始化配置的数据卷类型。提供两种选项,分别是ISO9660和FAT,该参数根据相关镜像安装和配置文档推荐选择。
Configuration Disk Volume Name:数据卷的名称。通常命名为disk。
ADD FILE参数:
Name:初始化配置命名。
Content:初始化配置内容。
四、Cases
通过例举相关用例,熟悉Node Definitions和Image Definitions的操作。
1、Cisco Catalyst 8000v
Catalyst 8000v 所需的硬件资源:
≥ 1 vCPU
≥ 4 RAM(GiB)
从 Catalyst 8000v Download 下载包含"-serial"字段的镜像,而不是EFI镜像。
以下是Catalyst 8000v ‘s Node Definition:
id: cat8000v
configuration:
generator:
driver: csr1000v
provisioning:
volume_name: disk
media_type: iso
files:
- name: iosxe_config.txt
content: |-
platform console serial
!
hostname insert_hostname_here
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
end
editable: true
inherited:
image:
ram: true
cpus: true
data_volume: false
boot_disk_size: false
cpu_limit: true
node:
ram: true
cpus: true
data_volume: false
boot_disk_size: false
cpu_limit: true
device:
interfaces:
has_loopback_zero: true
default_count: 4
loopback:
- Loopback0
physical:
- GigabitEthernet1
- GigabitEthernet2
- GigabitEthernet3
- GigabitEthernet4
- GigabitEthernet5
- GigabitEthernet6
- GigabitEthernet7
- GigabitEthernet8
- GigabitEthernet9
- GigabitEthernet10
- GigabitEthernet11
- GigabitEthernet12
- GigabitEthernet13
- GigabitEthernet14
- GigabitEthernet15
- GigabitEthernet16
- GigabitEthernet17
- GigabitEthernet18
- GigabitEthernet19
- GigabitEthernet20
- GigabitEthernet21
- GigabitEthernet22
- GigabitEthernet23
- GigabitEthernet24
- GigabitEthernet25
- GigabitEthernet26
serial_ports: 2
general:
description: Catalyst 8000V Edge Software
nature: router
read_only: false
schema_version: 0.0.1
sim:
linux_native:
cpus: 1
disk_driver: virtio
driver: csr1000v
libvirt_domain_driver: kvm
nic_driver: virtio
ram: 4096
cpu_limit: 100
boot:
timeout: 250
completed:
- Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog?
- Press RETURN to get started!
- '%CVAC-4-CONFIG_DONE:'
pyats:
os: iosxe
series: csr1000v
config_extract_command: show run
use_in_testbed: true
ui:
description: |-
Catalyst 8000V Edge Software
4 GB DRAM, 1 vCPU
[CCO Link](https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/routers/catalyst-8000v-edge-software/index.html)
group: Cisco
icon: router
label: CAT8000V
label_prefix: cat8000v-
visible: true2、Cisco Catalyst 9800
Catalyst 9800 所需的硬件资源:
≥ 2 vCPU
≥ 8 RAM(GiB)
从 Catalyst 9800 Download 下载镜像。
以下是Catalyst 9800 ‘s Node Definition:
id: cat9800
configuration:
generator:
driver: csr1000v
provisioning:
volume_name: disk
media_type: iso
files:
- name: iosxe_config.txt
content: hostname inserthostname_here
editable: true
device:
interfaces:
has_loopback_zero: true
default_count: 4
loopback:
- Loopback0
physical:
- GigabitEthernet1
- GigabitEthernet2
- GigabitEthernet3
- GigabitEthernet4
- GigabitEthernet5
- GigabitEthernet6
- GigabitEthernet7
- GigabitEthernet8
serial_ports: 2
inherited:
image:
ram: true
cpus: true
data_volume: false
boot_disk_size: false
node:
ram: true
cpus: true
data_volume: false
boot_disk_size: false
general:
description: Cisco Catalyst 9800 Wireless Controller for Cloud
nature: switch
read_only: true
schema_version: 0.0.1
boot:
timeout: 300
completed:
- 'Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog? [yes/no]:'
- '%SYS-5-RESTART: System restarted'
- 'INFO: Press RETURN to get started!'
sim:
linux_native:
cpus: 2
disk_driver: virtio
driver: server
libvirt_domain_driver: kvm
nic_driver: virtio
ram: 8192
video:
memory: 16
pyats:
os: iosxe
series: csr1000v
config_extract_command: show run
ui:
description: |-
Cisco Catalyst 9800 Wireless Controller for Cloud
8 GB DRAM, 2 vCPU
[CCO Link](https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/wireless/catalyst-9800-wireless-controllers-cloud/tsd-products-support-series-home.html)
group: Others
icon: access_point
label: Cat9800
label_prefix: cat9800-
visible: true3、FortiGate v6
FGT v6 所需的硬件资源:
≥ 1 vCPU
≥ 1 RAM(GiB)
以下是FGT v6 ‘s Node Definition:
id: fortigate
boot:
timeout: 60
completed:
- FortiGate-VM64-KVM login
configuration:
generator:
driver: null
provisioning:
files:
- name: meta-data
content: ''
editable: true
media_type: iso
volume_name: disk
device:
interfaces:
default_count: 4
has_loopback_zero: false
physical:
- port1
- port2
- port3
- port4
- port5
- port6
- port7
- port8
- port9
- port10
- port11
- port12
- port13
- port14
- port15
- port16
serial_ports: 1
general:
description: FortiGate Next Generation Firewall
nature: firewall
read_only: true
inherited:
image:
boot_disk_size: false
cpus: true
data_volume: true
ram: true
node:
boot_disk_size: false
cpus: true
data_volume: true
ram: true
pyats:
os: linux
schema_version: 0.0.1
sim:
linux_native:
cpus: 1
data_volume: 32
disk_driver: virtio
driver: server
libvirt_domain_driver: kvm
nic_driver: virtio
ram: 1024
ui:
description: |-
FortiGate Next Generation Firewall
1,024 MB DRAM, 1 vCPU
group: Others
icon: firewall
label: FortiGate
label_prefix: fortigate-
visible: true4、F5 BIGIP-VE
F5 BIGIP-VE 所需的硬件资源:
≥ 4 vCPU
≥ 4 RAM(GiB)
以下是F5 BIGIP-VE ‘s Node Definition:
id: f5-bigip-ve
general:
nature: server
read_only: false
description: F5 BIGIP Virtual Edition
device:
interfaces:
has_loopback_zero: false
physical:
- eth0
- eth1
- eth2
- eth3
- eth4
- eth5
- eth6
- eth7
- eth8
- eth9
- eth10
- eth11
- eth12
- eth13
- eth14
- eth15
- eth16
- eth17
- eth18
- eth19
- eth20
- eth21
- eth22
- eth23
- eth24
- eth25
- eth26
- eth27
serial_ports: 1
default_count: 4
ui:
visible: true
label_prefix: bigip-
icon: server
label: F5 BIGIP-VE
description: BIG-IP VE Appliance
sim:
linux_native:
libvirt_domain_driver: kvm
driver: server
disk_driver: virtio
ram: 4096
cpus: 4
nic_driver: virtio
video:
memory: 1
boot:
timeout: 600
completed:
- 'login: '
inherited:
image:
ram: true
cpus: true
data_volume: false
boot_disk_size: false
node:
ram: true
cpus: true
data_volume: false
boot_disk_size: false
configuration:
generator:
driver: null
provisioning:
volume_name: config-2
media_type: iso
files:
- name: user_data
editable: true
content: |-
#cloud-config
write_files:
- path: /config/onboarding/day0.sh
permissions: 0755
owner: root:root
content: |
#!/bin/sh
tmsh modify sys global-settings hostname mybigip.example.com
runcmd: [nohup sh -c '/config/onboarding/day0.sh' &]
- name: meta_data.json
editable: true
content: '{ "uuid": "1d9d6d3a-1d36-4db7-8d7c-63963d4d6f20", "hostname": "localhost"
}'
schema_version: 0.0.15、Cisco WSA
Cisco WSA S100V 所需的硬件资源:
≥ 3 vCPU
≥ 8 RAM(GiB)
从Cisco WSA Download下载镜像。
以下是Cisco WSA ‘s Node Definition:
id: wsa
general:
description: Cisco Web Security Appliance (WSA)
nature: server
read_only: false
device:
interfaces:
has_loopback_zero: true
physical:
- enp6s0
- enp6s1
- enp6s2
- enp6s3
serial_ports: 2
default_count: 4
loopback:
- loopback
ui:
visible: true
label_prefix: wsa-
icon: server
label: WSA
description: |-
Cisco Web Security Appliance (WSA)
8192 MB RAM, 3 vCPUs
sim:
linux_native:
libvirt_domain_driver: kvm
driver: server
disk_driver: ide
ram: 8192
cpus: 3
cpu_limit: 100
nic_driver: virtio
boot:
timeout: 300
inherited:
image:
ram: true
cpus: true
cpu_limit: true
data_volume: true
boot_disk_size: true
node:
ram: true
cpus: true
cpu_limit: true
data_volume: true
boot_disk_size: true
configuration:
generator:
driver: server
provisioning:
volume_name: cidata
media_type: iso
files:
- name: config.xml
editable: true
content: |-
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?>
<!DOCTYPE config SYSTEM "config.dtd">
<config>
</config>
schema_version: 0.0.16、Cisco Nexus 9500
Cisco Nexus 9500 148 Ports所需的硬件资源:
≥ 4 vCPU
≥ 16 RAM(GiB)
从 Cisco Nexus 9500 下载镜像。
以下是Cisco Nexus 9500 ‘s Node Definition:
id: nxosv9500-148
configuration:
generator:
driver: nxosv9000
provisioning:
volume_name: disk
media_type: iso
files:
- name: nxos_config.txt
editable: true
content: |-
#insert hostname
platform insert module 2 linecard N9K-X9516v
platform insert module 3 linecard N9K-X9532v
platform insert module 4 linecard N9K-X9536v
device:
interfaces:
has_loopback_zero: true
default_count: 4
loopback:
- Loopback0
management:
- mgmt0
physical:
- mgmt0
- Ethernet1/1
- Ethernet1/2
- Ethernet1/3
- Ethernet1/4
- Ethernet1/5
- Ethernet1/6
- Ethernet1/7
- Ethernet1/8
- Ethernet1/9
- Ethernet1/10
- Ethernet1/11
- Ethernet1/12
- Ethernet1/13
- Ethernet1/14
- Ethernet1/15
- Ethernet1/16
- Ethernet1/17
- Ethernet1/18
- Ethernet1/19
- Ethernet1/20
- Ethernet1/21
- Ethernet1/22
- Ethernet1/23
- Ethernet1/24
- Ethernet1/25
- Ethernet1/26
- Ethernet1/27
- Ethernet1/28
- Ethernet1/29
- Ethernet1/30
- Ethernet1/31
- Ethernet1/32
- Ethernet1/33
- Ethernet1/34
- Ethernet1/35
- Ethernet1/36
- Ethernet1/37
- Ethernet1/38
- Ethernet1/39
- Ethernet1/40
- Ethernet1/41
- Ethernet1/42
- Ethernet1/43
- Ethernet1/44
- Ethernet1/45
- Ethernet1/46
- Ethernet1/47
- Ethernet1/48
- Ethernet1/49
- Ethernet1/50
- Ethernet1/51
- Ethernet1/52
- Ethernet1/53
- Ethernet1/54
- Ethernet1/55
- Ethernet1/56
- Ethernet1/57
- Ethernet1/58
- Ethernet1/59
- Ethernet1/60
- Ethernet1/61
- Ethernet1/62
- Ethernet1/63
- Ethernet1/64
- Ethernet2/1
- Ethernet2/2
- Ethernet2/3
- Ethernet2/4
- Ethernet2/5
- Ethernet2/6
- Ethernet2/7
- Ethernet2/8
- Ethernet2/9
- Ethernet2/10
- Ethernet2/11
- Ethernet2/12
- Ethernet2/13
- Ethernet2/14
- Ethernet2/15
- Ethernet2/16
- Ethernet3/1
- Ethernet3/2
- Ethernet3/3
- Ethernet3/4
- Ethernet3/5
- Ethernet3/6
- Ethernet3/7
- Ethernet3/8
- Ethernet3/9
- Ethernet3/10
- Ethernet3/11
- Ethernet3/12
- Ethernet3/13
- Ethernet3/14
- Ethernet3/15
- Ethernet3/16
- Ethernet3/17
- Ethernet3/18
- Ethernet3/19
- Ethernet3/20
- Ethernet3/21
- Ethernet3/22
- Ethernet3/23
- Ethernet3/24
- Ethernet3/25
- Ethernet3/26
- Ethernet3/27
- Ethernet3/28
- Ethernet3/29
- Ethernet3/30
- Ethernet3/31
- Ethernet3/32
- Ethernet4/1
- Ethernet4/2
- Ethernet4/3
- Ethernet4/4
- Ethernet4/5
- Ethernet4/6
- Ethernet4/7
- Ethernet4/8
- Ethernet4/9
- Ethernet4/10
- Ethernet4/11
- Ethernet4/12
- Ethernet4/13
- Ethernet4/14
- Ethernet4/15
- Ethernet4/16
- Ethernet4/17
- Ethernet4/18
- Ethernet4/19
- Ethernet4/20
- Ethernet4/21
- Ethernet4/22
- Ethernet4/23
- Ethernet4/24
- Ethernet4/25
- Ethernet4/26
- Ethernet4/27
- Ethernet4/28
- Ethernet4/29
- Ethernet4/30
- Ethernet4/31
- Ethernet4/32
- Ethernet4/33
- Ethernet4/34
- Ethernet4/35
- Ethernet4/36
serial_ports: 2
inherited:
image:
ram: true
cpus: true
data_volume: false
cpu_limit: true
boot_disk_size: false
node:
ram: true
cpus: true
cpu_limit: true
data_volume: false
boot_disk_size: false
general:
description: Cisco Nexus 9500v Switch 148 Ports
nature: switch
read_only: false
schema_version: 0.0.1
sim:
linux_native:
cpus: 4
disk_driver: sata
driver: nxosv9000
efi_boot: true
libvirt_domain_driver: kvm
nic_driver: e1000
ram: 16384
cpu_limit: 100
boot:
timeout: 480
completed:
- There is no admin password in the bootstrap file
- User Access Verification
pyats:
os: nxos
series: n9k
config_extract_command: show run
use_in_testbed: true
ui:
description: |-
Cisco Nexus 9500v Switch with 148 Ports
Line cards inserted in the following sequence
Module 1 Nexus 9500v 64 port Ethernet1/1 - Ethernet1/64 (Default)
Module 2 Nexus 9500v 16 port Ethernet2/1 - Ethernet2/16
Module 3 Nexus 9500v 32 port Ethernet3/1 - Ethernet3/32
Module 4 Nexus 9500v 36 port Ethernet4/1 - Ethernet4/36
Requires 16 GB DRAM, 4 vCPUs
group: Cisco
icon: switch
label: NX-OS 9500-148
label_prefix: nxos9500-148-
visible: trueIf you need to add more node definitions, please see the public to cml-community repository download additional node definitions or to share ones you have created.

评论